Managing data effectively is essential for any business. In today’s digital world, companies amass large amounts of data and accessing, storing, and managing it properly is essential to make use of the information. Business process outsourcing services such as data entry, data cleansing and document scanning play a key role in helping businesses manage their data processing tasks. With evolving technologies like automation, machine learning, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, companies need to know how to extract value from their data to make the most of it. The value of data depends on its quality. Today, companies have realized the value of high-quality data when it comes to taking quick and smart decisions to stay competitive. So, what does ‘data quality’ imply and what is its significance?
What Is Data Quality?
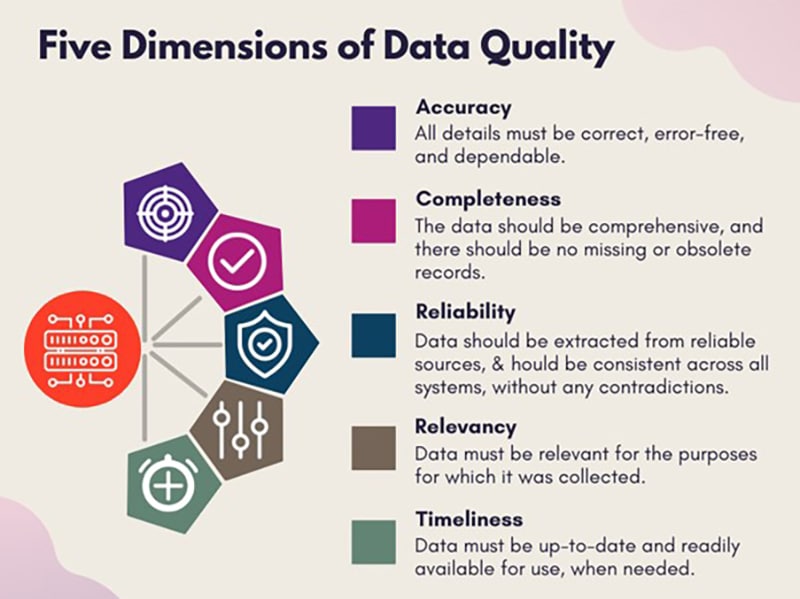
Data quality is defined based on characteristics such as accuracy, consistency, completeness, reliability, and whether it’s up to date. Companies need to identify data errors that need to be resolved and see whether their digital data can meet its intended purpose. However, data quality is not as good as it should be. A Harvard Business Review study reported that data quality is far worse than most companies realize, and that a mere 3% of the data quality scores in the study were rated as “acceptable” (www.forbes.com).
Common Causes of Poor Data Quality
- Data entry errors: Errors in manual and even automated data entry are the most common causes of poor quality data. Mistakes can occur while typing a Word document or when entering information into an Excel spreadsheet. In addition to typographical errors, data entry errors include repetition and deletion. They happen when you hit the wrong key or use a program with autocorrect. Transposition errors are usually related to numbers, for e.g. typing 564 instead of 546.
- Lack of proper data entry standards: Data entry standards are necessary to ensure database records that are consistent, complete and accurate. Data entry standards include instructions relating to indexing individuals’ names, data field restrictions, how names of individuals should be written, business/organization name rules, etc. Operators working on a data entry project must comply with a minimum set of standards that are compatible with the data entry system used and the data input sources.
- Incomplete information: Incomplete or missing information can make data unusable. Missing data means rows or columns have null, blank or incomplete values. Missing data includes missing last names, phone numbers, email addresses, and age. Poor data standards (web forms without mandatory fields) and participants dropping out of the study are common reasons for missing data. This can be due to a human factor (such as a person not responding to a survey question).
- Data decay: Data decay is the deterioration of data so that it is no longer usable. It occurs when data loses it integrity, completeness, and accuracy because it was not maintained. For example, company information, personal details, contact details and other data can become unfit for use over time. HubSpot estimated that email marketing databases naturally degrade by 22.5% approximately every year. Organizations can and should take steps to detect and clean decayed data and solve the problem.
- Data silos: Data silos are data available only to certain departments of an organization. When organizations use multiple apps and systems to manage various workflows, it leads to the development of data silos that make it difficult for teams to find the information they need. It can also lead to duplicate data in different departments. Data silos lead to poor decision-making, more errors and weaker team morale and revenue, according to a new Airtable-commissioned study by Forrester Consulting (www.venturebeat.com). Up to 79% of knowledge workers said that teams throughout their organizations are siloed, and 68% described their work as negatively impacted because they don’t have visibility into cross-functional projects.
- Failed data migration: Managing data requires moving it between different storage types, formats, data architectures and enterprise systems. Data migration to one unified location makes it much more organized and easier for teams to access. On the other hand, failed migration can lead to missing, invalid or inconsistent legacy data that can cause critical process disruptions.
- Poor data governance: Data governance involves managing data quality, usability and integrity from capture to application. Proper data governance ensures clean, consistent, and trustworthy information assets to drive analytics and decision making, optimize operations, and boost business growth. Bad data governance leads to inaccurate, insufficient or out-of-date data and impacts overall operations, productivity, and revenue.
- Process inefficiencies: Persistent problems such as missing data and data redundancies can lead to process inefficiencies upstream, which will significantly affect work downstream.
Costs of Poor Data
Gartner estimates that poor data quality costs organizations an average $12.9 million every year. Poor data poses many business risks: inaccurate analysis, missed opportunities, poor decision making, reduced efficiency, customer attrition, reputational damage, revenue loss, and compliance issues.
“Data quality is directly linked to the quality of decision making. Good quality data provides better leads, better understanding of customers and better customer relationships,” says Melody Chien, Senior Research Director, Gartner.
- Impacts all departments across the organization: As an organization expands, its data gets redistributed to different departments and systems. So, even a small error can have a devastating ripple effect. Errors in customer information can trickle down to the accounts department, marketing, and other sections.
- Leads to customer attrition: Poor data can wreck the customer experience. Mistakes in contact information or a misspelled customer name can damage customer relationships and lead to customer attrition, and impact your marketing campaign. Moreover, if customer contact details are incorrect or incomplete and a salesperson has to call customers to verify the information, it can waste their time.
- Delayed business decisions and lost opportunities: Poor data quality delays response to situations. For instance, decision makers can address issues and take the right action to respond to market changes promptly only if they have quality data at their fingertips.
- Financial risks: If you are working to introduce new initiatives, find new sources of revenue, optimize resource use, and increase sales and profits, poor data can hamper your efforts. Research shows that the financial impact of bad data is more than $3 trillion per year in the US.
- Impacts compliance and regulatory reporting: Organizations have to submit data to relevant authorities to demonstrate compliance with regulations. Poor data quality can affect regulatory, risk, and management reporting.
Outsourcing Solutions Can Support Good Data Governance
Be it a database or a customer relationship management (CRS) system, even seemingly insignificant mistakes such as a single letter, punctuation mark or space in the wrong place can have an enormous impact. It can negatively affect everything from an email marketing campaign to customer service and eventually, revenue generation.
Outsourcing services such as data entry and data conversion focus on helping businesses ensure high quality data. This is critical for implementing emerging technologies like robotic process automation (RPA) to drive robust data management and create greater business value.
Outsourcing benefits include:
- Increase revenue: Reliable data entry and conversion support will drive proper data management and increase efficiency, productivity and revenue.
- Lower costs: Automation and analytics will improve resource use and process efficiencies and reduce or even eliminate costs.
- Mitigate risks: Proper data governance will promote compliance, security and privacy.
From data entry to data conversion, Managed Outsource Solutions ensures high-quality data that drives efficiency, productivity, and revenue.
Companies can leverage advanced technologies to store, process and analyze their data and take meaningful decisions to boost growth and revenue. Relying on an experienced business process outsourcing company for data cleansing, data entry, document scanning and conversion is a practical option to prepare large volumes of data for such analysis. Working with the right partner can help organizations stay better equipped to keep their data clean and well-organized at all times.