The advantages of digital preservation of paper-based documents with the assistance of document conversion services are well recognized and accepted today. Records in digital format are easier to preserve, backup, organize, and share and significantly reduce physical storage space requirements. The concept of digitization is gaining importance not only due to these ensured advantages but also due to the need for the long-term preservation and security of critical documents.
Tips for Secure Data Storage and Record Retention
Importance of Secure Data Storage and Record Retention
Sensitive information can be kept on computers, storage devices, websites, and the cloud by any business or organization. Although stored data is essential to corporate operations, if it is not safeguarded, it may also become a liability. In the absence of a sufficient data protection policy, hackers may obtain sensitive information and use it to breach your network, conduct business espionage, or reveal the private information of your clients or staff. Safe data storage entails guarding against unauthorized users and uses, intentional or unintentional damage or destruction, and theft or unauthorized use of storage resources and the data stored on them, whether on-site, off-site, or in cloud computing environments. Enterprises must pay close attention to this sector because it is ultimately responsible for the majority of data breaches.
Another crucial component of data management is data retention, which makes sure that pertinent data is preserved for the necessary length of time. In addition to helping firms avoid future lawsuits or investigations, data retention can also help them comply with legal and regulatory requirements. A common practice among certain businesses is to hold onto data that is no longer needed in case it becomes necessary in the future. Organizations should consider the costs of keeping superfluous data, such as storage and security costs, given the increasing volume of data generated daily. For this reason, businesses ought to implement an appropriate data retention strategy. Organizations can limit the amount of data they retain to that which is required for the purposes for which it was obtained by implementing retention rules and procedures. Retention policies specify the kinds of information that an organization keeps, how it is used, and how long it should be kept on file.
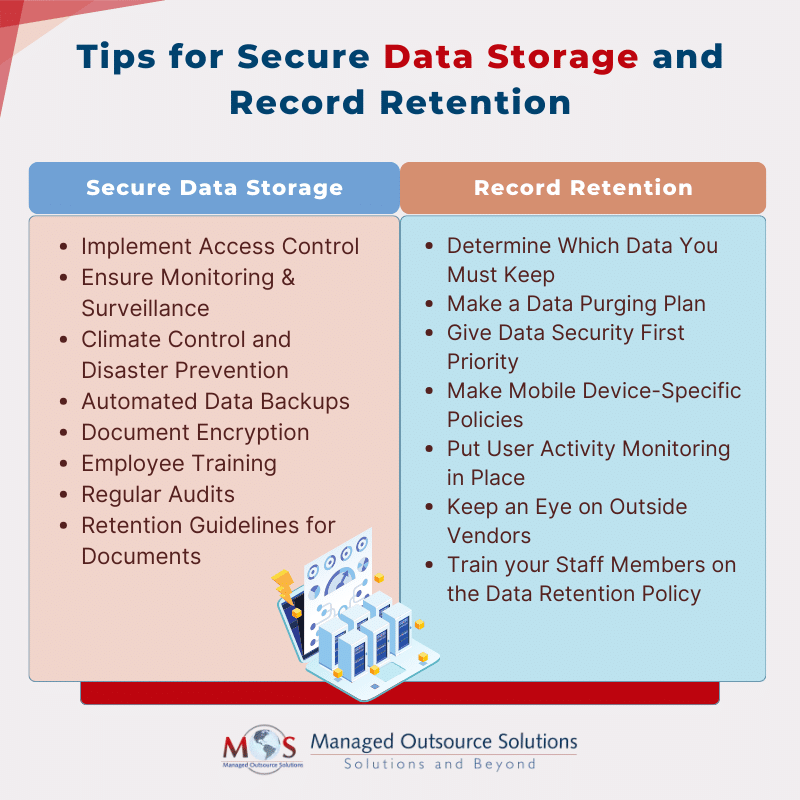
Ensuring Secure Data Storage
Some tips to ensure secure data storage:
- Access Control: Give your document management system strict access control methods. Your records can only be viewed, edited, and shared by authorized personnel.
- Monitoring & Surveillance: To guarantee that your papers are always safe in the facility, off-site storage provides live patrols and round-the-clock surveillance. Your records can also be retrieved at any time thanks to this.
- Climate Control and Disaster Prevention: Controlling the right temperature and humidity in your data storage environment also protects against potential risks and stops document deterioration. Eisaster recovery plans and fire suppression systems shield your records from unanticipated crises.
- Automated Data Backups: Ensure digital documents are regularly backed up and securely stored offsite. This safety measure guarantees that your important data will not be lost in the event of an unforeseen circumstance.
- Document Encryption: Protect digital documents from unwanted access by using encryption. Encryption preserves the confidentiality and integrity of your critical information, especially against external attacks.
- Employee Training: Provide your staff with training on safe record-keeping and security protocols. Employees that are aware and watchful are your first line of protection against security risks.
- Regular Audits: Perform regular security audits to find weak points and locations where your records storage system needs to be improved. This will help you develop and improve your system over time.
- Retention Guidelines for Documents: Create and implement transparent document retention policies that outline the proper time for retention.
Read our blog post about The Roadmap to Digital Transformation: How to Implement Document Digitization
Data Retention Policy Tips
Some tips to consider when planning your data retention policy:
- Determine which data you must keep: Making a list of the data in your organization and determining what needs to be stored is the first step. Depending on your industry, the way your organization operates, and the criteria for compliance, requirements may change. For instance, healthcare facilities in Nevada are required to retain patient records for a minimum of five years.
- Make a data purging plan: What will happen to the data when the retention period ends? Will you destroy it or will you keep holding onto it? Do you plan to automate this procedure or handle it manually? After making a plan, search for resources that will enable you to speed up the procedure. For retention and purging policies, automation frequently offers the best option.
- Give data security first priority: It is imperative that your data retention policy incorporates measures to avert data breaches and unapproved access. This could include methods for preventing data loss, physical security measures, and data encryption. Too many businesses put off giving cybersecurity a real priority until there is a breach. Some may decide to cut costs by investing less in cybersecurity. Cleaning up after a data breach, however, is always more costly. According to Forbes, each hack costs $4.24 million on average.
- Make mobile device-specific policies: With the growing trend of “bring your own device” in many organizations, it’s critical to establish policies that address data saved on personal devices.
- Put user activity monitoring in place: Understanding how users are using data is essential to ensuring data safety. With the use of tools for tracking user behavior, it is feasible to spot any suspicious activities. These tools can also be used by managers to enforce data retention guidelines. For instance, the system may prevent a user from downloading files that your data retention policy has designated for removal.
- Keep an eye on outside vendors: Third-party providers who have access to your data should be covered by your policy. Financial data and client records may be included in this data. It should be mandatory for these third parties to sign contracts that specify how they will protect data. It is imperative that you establish protocols to oversee their adherence to these agreements.
- Train your staff members on your Data Retention Policy: Every employee needs to understand the policy and how they fit into it. Data entry personnel, customer service agents, supervisors, and executives should be given top priority. Workers should be aware of the types of data they must retain and how long. When the time comes, they should also be aware of how to access this data and the steps to take to remove it.
- Review and update the policy on a regular basis: Policies on data retention must adapt to the rapid changes in technology. Changes in compliance standards is another possibility. Regular evaluations and changes are necessary to stay current. Staying on top of emerging cybersecurity dangers and modifications to data storage techniques is also essential.
Transform your document management process with our professional document scanning services today.
Record retention and secure data storage are of paramount importance in today’s digital age, especially in industries like healthcare, finance, and legal services. Document conversion services play a crucial role in ensuring that sensitive information is stored securely and accessible when needed. By converting physical documents into digital formats, businesses can not only save physical space but also reduce the risk of loss or damage to important records. Similarly, records should be retained as per the retention schedule laid down by laws and regulations. Both of these techniques protect the privacy of clients and customers but also helps companies comply with regulatory requirements such as GDPR or HIPAA.